
In most cases, neurons are generated by neural stem cells during brain development and childhood.
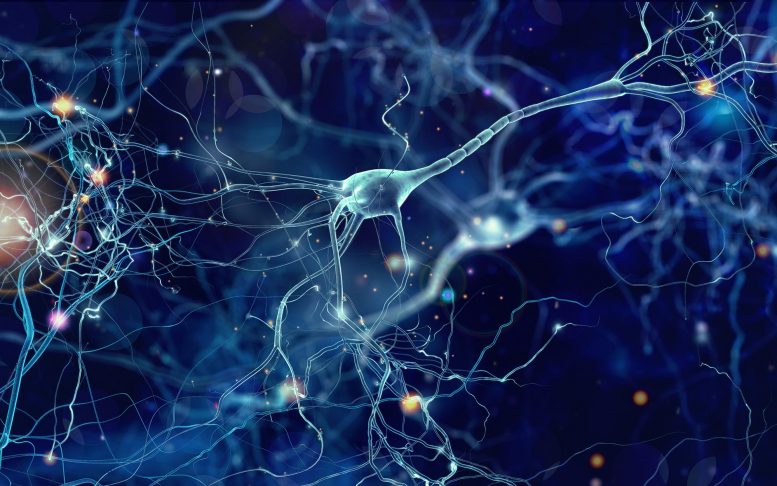
Synaptic signals may be excitatory or inhibitory, increasing or reducing the net voltage that reaches the soma. This potential travels rapidly along the axon and activates synaptic connections as it reaches them. If the voltage changes by a large enough amount over a short interval, the neuron generates an all-or-nothing electrochemical pulse called an action potential. Neurons are electrically excitable, due to maintenance of voltage gradients across their membranes. The signaling process is partly electrical and partly chemical. However, synapses can connect an axon to another axon or a dendrite to another dendrite. At the majority of synapses, signals cross from the axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another. Most neurons receive signals via the dendrites and soma and send out signals down the axon. The term neurite is used to describe either a dendrite or an axon, particularly when the cell is undifferentiated. Neurons may lack dendrites or have no axon. At the farthest tip of the axon's branches are axon terminals, where the neuron can transmit a signal across the synapse to another cell. It branches but usually maintains a constant diameter. The axon leaves the soma at a swelling called the axon hillock and travels for as far as 1 meter in humans or more in other species. Dendrites typically branch profusely and extend a few hundred micrometers from the soma. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dendrites are filaments extruding from the soma. When multiple neurons are functionally connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit.Ī typical neuron consists of a cell body ( soma), dendrites, and a single axon. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord.
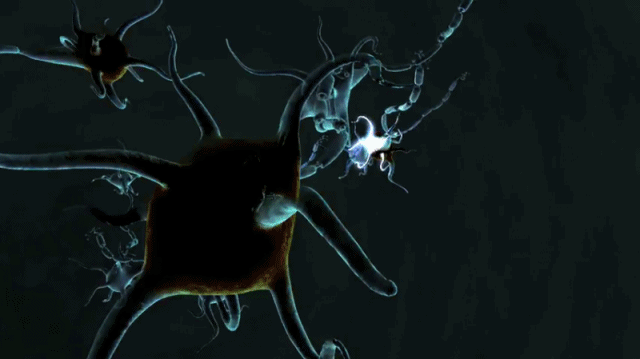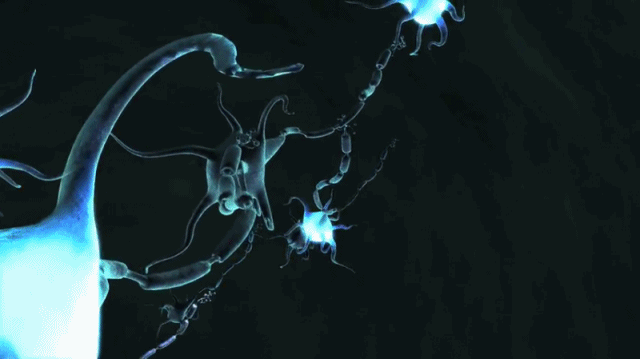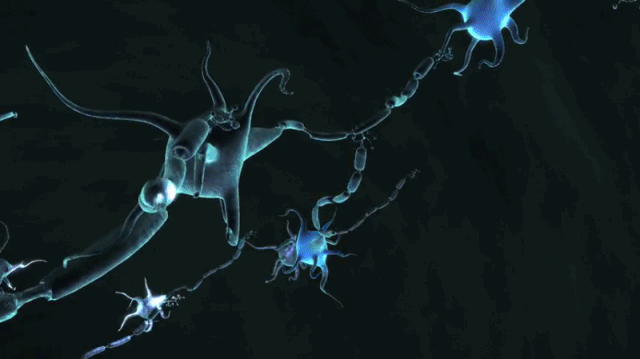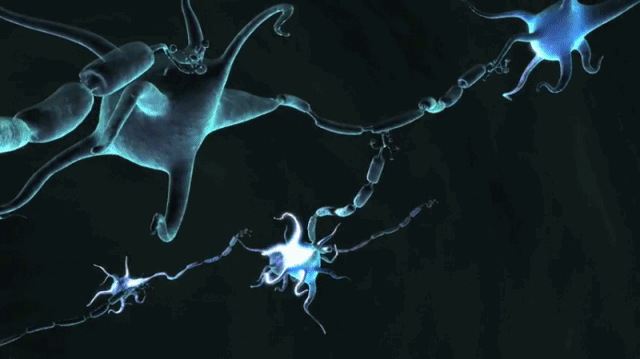
Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses - specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Within a nervous system, a neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
